
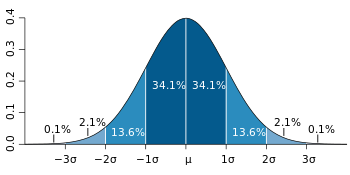

Because the normal distribution is a continuous distribution, we can not calculate exact probability for an outcome, but instead we calculate a probability for a range of outcomes (for example the probability that a random variable X is greater than 10). The normal probability distribution, one of the fundamental continuous distributions of statistics, is actually a family of distributions (an infinite number of distributions with differing means (μ) and standard deviations (σ). Further, we know that the area under the curve from negative infinity to positive infinity is one. A probability density function is defined such that the likelihood of a value of X between a and b equals the integral (area under the curve) between a and b. Probability distributions may either be discrete (distinct/separate outcomes, such as number of children) or continuous (a continuum of outcomes, such as height). The probability that X falls between two values (a and b) equals the integral (area under the curve) from a to b:Ī probability distribution is formed from all possible outcomes of a random process (for a random variable X) and the probability associated with each outcome. The normal distribution is one example of a continuous distribution. Therefore we often speak in ranges of values (p(X>0) =. Because there are infinite values that X could assume, the probability of X taking on any one specific value is zero. Continuous probability distribution : A probability distribution in which the random variable X can take on any value (is continuous).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
